
/* nicolas.janey@univ-fcomte.fr */
/* Octobre 2005 */
/* Classe de gestion de vecteurs */
/* a quatre coordonnees */
#ifndef VECTEURT
#define VECTEURT
class VecteurT {
public :
float m[4];
public :
VecteurT(void);
VecteurT(float x,float y,float z,float t);
VecteurT(float *m);
~VecteurT(void);
void print(void);
};
#endif
/* nicolas.janey@univ-fcomte.fr */
/* Novembre 2005 */
/* Classe de gestion de vecteurs */
/* a quatre coordonnees */
#include <stdio.h>
#include "VecteurT.h"
VecteurT::VecteurT(void) {
this->m[0] = this->m[1] =this->m[2] = this->m[3] = 0.0F;
}
VecteurT::VecteurT(float x,float y,float z,float t) {
this->m[0] = x;
this->m[1] = y;
this->m[2] = z;
this->m[3] = t;
}
VecteurT::VecteurT(float *m) {
this->m[0] = m[0];
this->m[1] = m[1];
this->m[2] = m[2];
this->m[3] = m[3];
}
VecteurT::~VecteurT(void) {
}
void VecteurT::print(void) {
printf("%8.3f%8.3f%8.3f%8.3f\n",m[0],m[1],m[2],m[3]);
}
/* nicolas.janey@univ-fcomte.fr */
/* Novembre 2005 */
/* Classe de gestion */
/* de transformations geometriques */
#ifndef TRANSFORMATIONT
#define TRANSFORMATIONT
#include "VecteurT.h"
class TransformationT {
public :
float m[4][4];
public :
TransformationT(void);
TransformationT(float m[4][4]);
~TransformationT(void);
void compose(VecteurT *v);
void compose(TransformationT *t);
void print(void);
};
#endif
/* nicolas.janey@univ-fcomte.fr */
/* Novembre 2005 */
/* Classe de gestion */
/* de transformations geometriques */
/* en coordonnees homogenes */
#include <stdio.h>
#include "TransformationT.h"
#include "VecteurT.h"
TransformationT::TransformationT(void) {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++ )
for ( int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; j++ )
m[i][j] = ( i == j ) ? 1.0F : 0.0F;
}
TransformationT::TransformationT(float m[4][4]) {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++ )
for ( int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; j++ )
this->m[i][j] = m[i][j];
}
TransformationT::~TransformationT(void) {
}
void TransformationT::compose(VecteurT *v) {
VecteurT *nv = new VecteurT();
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++ )
for ( int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; j++ )
nv->m[i] += m[i][j]*v->m[j];
*v = *nv;
delete(nv);
}
void TransformationT::compose(TransformationT *t) {
TransformationT *nt = new TransformationT();
{ for ( int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++ )
for ( int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; j++ ) {
nt->m[i][j] = 0;
for ( int k = 0 ; k < 4 ; k++ )
nt->m[i][j] += t->m[i][k]*m[k][j]; } }
{ for ( int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++ )
for ( int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; j++ )
m[i][j] = nt->m[i][j]; }
delete(nt);
}
void TransformationT::print(void) {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++ )
printf("%8.3f%8.3f%8.3f%8.3f\n",m[i][0],m[i][1],m[i][2],m[i][3]);
}
Le source : ExamTD120052006Exo1.cpp
/* Auteur: Nicolas JANEY */
/* nicolas.janey@univ-fcomte.fr */
/* Novembre 2005 */
/* Test de classes de representation */
/* de vecteurs et de transformations */
/* geometriques en coordonnees homogenes */
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "TransformationT.h"
#include "VecteurT.h"
int main(int argc,char **argv) {
VecteurT *v1 = new VecteurT( 0.0F, 0.0F, 0.0F, 1.0F);
VecteurT *v2 = new VecteurT( 1.0F, 1.0F, 1.0F, 0.0F);
VecteurT *v3 = new VecteurT( 2.0F, -4.0F, 3.0F, -6.0F);
float cs =(float) cos(1.0);
float sn =(float) sin(1.0);
float m1[4][4] = { { cs, -sn, 0.0F, 0.0F },
{ sn, cs, 0.0F, 0.0F },
{ 0.0F, 0.0F, 1.0F, 0.0F },
{ 0.0F, 0.0F, 0.0F, 1.0F } };
float m2[4][4] = { { 1.0F, 0.0F, 0.0F, -3.0F },
{ 0.0F, 1.0F, 0.0F, 2.0F },
{ 0.0F, 0.0F, 1.0F, 5.0F },
{ 0.0F, 0.0F, 0.0F, 1.0F } };
float m3[4][4] = { { 1.0F, 2.0F,-3.0F, -1.0F },
{ -2.0F, 3.0F, 1.0F, 4.0F },
{ -1.0F,-1.0F, 4.0F, 7.0F },
{ 0.0F, 0.0F, 0.0F, 1.0F } };
TransformationT *t1 = new TransformationT(m1);
TransformationT *t2 = new TransformationT(m2);
TransformationT *t3 = new TransformationT(m3);
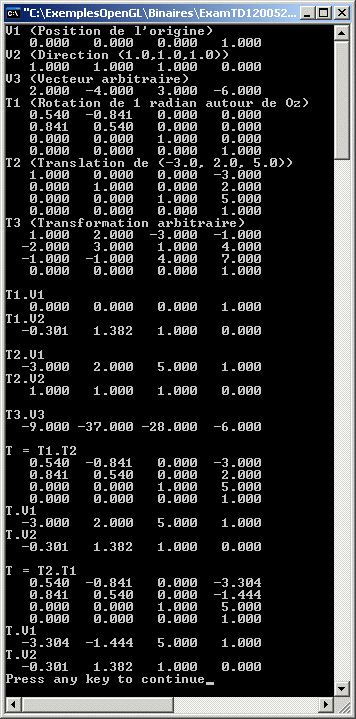
printf("V1 (Position de l'origine)\n");
v1->print();
printf("V2 (Direction (1.0,1.0,1.0))\n");
v2->print();
printf("V3 (Vecteur arbitraire)\n");
v3->print();
printf("T1 (Rotation de 1 radian autour de Oz)\n");
t1->print();
printf("T2 (Translation de (-3.0, 2.0, 5.0))\n");
t2->print();
printf("T3 (Transformation arbitraire)\n");
t3->print();
printf("\n");
printf("T1.V1\n");
t1->compose(v1);
v1->print();
printf("T1.V2\n");
t1->compose(v2);
v2->print();
delete(v1);
delete(v2);
printf("\n");
v1 = new VecteurT( 0.0F, 0.0F, 0.0F, 1.0F);
v2 = new VecteurT( 1.0F, 1.0F, 1.0F, 0.0F);
printf("T2.V1\n");
t2->compose(v1);
v1->print();
printf("T2.V2\n");
t2->compose(v2);
v2->print();
delete(v1);
delete(v2);
printf("\n");
printf("T3.V3\n");
t3->compose(v3);
v3->print();
printf("\n");
v1 = new VecteurT( 0.0F, 0.0F, 0.0F, 1.0F);
v2 = new VecteurT( 1.0F, 1.0F, 1.0F, 0.0F);
{ TransformationT *t = new TransformationT();
t->compose(t1);
t->compose(t2);
printf("T = T1.T2\n");
t->print();
printf("T.V1\n");
t->compose(v1);
v1->print();
printf("T.V2\n");
t->compose(v2);
v2->print();
delete(t); }
delete(v1);
delete(v2);
printf("\n");
v1 = new VecteurT( 0.0F, 0.0F, 0.0F, 1.0F);
v2 = new VecteurT( 1.0F, 1.0F, 1.0F, 0.0F);
{ TransformationT *t = new TransformationT();
t->compose(t2);
t->compose(t1);
printf("T = T2.T1\n");
t->print();
printf("T.V1\n");
t->compose(v1);
v1->print();
printf("T.V2\n");
t->compose(v2);
v2->print();
delete(t); }
delete(v1);
delete(v2);
delete(v3);
delete(t1);
delete(t2);
delete(t3);
return(0);
}