Renderman (Partie 2)
Transformations géométriques
Renderman inclut dans son environnement une transformation géométrique courante qui sera appliquée à tout objet nouvellement défini. Cette transformation géométrique peut être sauvée et restaurée.
void RiTransformBegin(void)
Sauvegarde
void RiTransformEnd(void)
Restauration
Transformations
Translation
void RiTranslate(RtFloat dx,RtFloat dy,RtFloat dz)
Translation de vecteur (dx,dy,dz)
Rotation
void RiRotate(RtFloat a,RtFloat dx,RtFloat dy,RtFloat dz)
Rotation d'angle a autour de l'axe (dx,dy,dz)
Zoom
void RiScale(RtFloat sx,RtFloat sy,RtFloat sz)
Zoom de rapports (sx,sy,sz) selon les axes x, y et z
Skew
void RiSkew(RtFloat a,RtFloat dx1,RtFloat dy1,RtFloat dz1,RtFloat dx2,RtFloat dy2,RtFloat dz2)
Rotation d'angle a entre deux directions orthogonales (dx1,dy1,dz1) et (dx2,dy2,dz2)
Perspective
void RiPerspective(RtFloat adv)
Mise en perspective avec un angle de vision adv selon l'axe +z
Transformation générique
void RiConcatTransform(RtMatrix t)
Concatène la transformation t avec la transformation courante
Promouvoir une nouvelle transformation courante
Identité
void RiIdentity(void)
Efface la transformation courante et la remplace par la transformation identité.
Transformation générique
void RiTransform(RtMatrix t)
Efface la transformation courante et la remplace par la transformation t.
Transformation non linéaire
void Deformation(char *name,paremeterlist)
Efface la transformation courante et la remplace par la transformation réalisée par le shader de nom name.
Modélisation hiérarchique
Solide : Objet représenté par ses bords <=> un ensemble de surfaces incluant un espace
L'union de ces surfaces ne doit pas présenter de trou de sorte que tout point de l'espace puisse être situé sans ambiguïté à l'intérieur ou à l'extérieur du solide.
Solide : assemblage de quadriques, polygones et surfaces paramétriques
Objets C.S.G.
Renderman permet la construction et l'affichage d'objets C.S.G. Ces objets sont appelés "solide composite".
Solide composite : composition hiérarchique de solides et d'autres solides composites
Un solide est défini et délimité par les instructions suivantes :
void RiSolidBegin(RtToken type) ;
void RiSolidEnd() ;
Le token type peut prendre quatre valeurs :
- RI_PRIMITIVE : définition d'un objet C.S.G.
- RI_UNION : union des objets
- RI_DIFFERENCE : retrait du deuxième objet au premier
- RI_INTERSECTION : intersection des objets
Exemples
/* Copyrighted Pixar 1989 */
/* From the RenderMan Companion */
#include <ri.h>
#include <math.h>
RtColor color = {.9F,.9F,.5F};
/* SolidCylinder() makes a solid cylinder
* of the given radius,extending
* from zmin to zmax along the z axis. */
void SolidCylinder(float radius,
float zmin,
float zmax) {
RiSolidBegin(RI_PRIMITIVE);
RiCylinder(radius,zmin,zmax,
360.0,RI_NULL);
RiDisk(zmax,radius,360.0,RI_NULL);
RiDisk(zmin,radius,360.0,RI_NULL);
RiSolidEnd();
}
/* SolidSphere: create a closed sphere */
void SolidSphere(float r,
float zmin,
float zmax) {
RiSolidBegin(RI_PRIMITIVE);
RiSphere(r,zmin,zmax,360.0,RI_NULL);
if ( fabs(zmax) < r )
RiDisk(zmax,
(float) sqrt(r*r-zmax*zmax),
360.0F,RI_NULL);
if ( fabs(zmin) < r )
RiDisk(zmin,
(float) sqrt(r*r-zmin*zmin),
360.0F,RI_NULL);
RiSolidEnd();
}
/* SolidHemisphere: create a solid
* hemisphere from a sphere
* and a cylinder*/
void SolidHemisphere(float radius,
float zmin,
float zmax) {
RiSolidBegin(RI_INTERSECTION);
SolidSphere(radius,zmin,zmax);
RiRotate(90.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidCylinder(radius,0.0,radius);
RiSolidEnd();
}
/* SolidWedge(r,zmin,zmax,thetamax):
* make a solid from a (partial)
* sphere as the intersection or
* union of two hemispheres. */
void SolidWedge(float r,
float zmin,
float zmax,
float thetamax) {
if (thetamax == 180.0) {
SolidHemisphere(r,zmin,zmax); }
else
if (thetamax == 360.0) {
SolidSphere(r,zmin,zmax); }
else
if (thetamax < 180.0) {
RiSolidBegin(RI_INTERSECTION);
SolidHemisphere(r,zmin,zmax);
RiRotate(thetamax-180.0F,
0.0F,0.0F,1.0F);
SolidHemisphere(r,zmin,zmax);
RiSolidEnd(); }
else
if (thetamax < 360.0) {
RiSolidBegin(RI_UNION);
SolidHemisphere(r,zmin,zmax);
RiRotate(thetamax,0.0,0.0,1.0);
SolidHemisphere(r,zmin,zmax);
RiSolidEnd(); }
}
void Go(void) {
RiColor(color);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(6.0,-6.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidWedge(1.5F,0.7F,-0.8F,260.0F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(2.0,-6.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidWedge(1.5F,0.7F,0.2F,260.0F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(-2.0,-6.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidWedge(1.5F,0.2F,-0.2F,260.0F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(-6.0,-6.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidWedge(1.0F,1.7F,-1.7F,260.0F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(6.0,-2.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidHemisphere(1.5F,0.7F,-0.8F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(2.0,-2.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidHemisphere(1.5F,0.7F,0.2F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(-2.0,-2.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidHemisphere(1.5F,0.2F,-0.2F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(-6.0,-2.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidHemisphere(1.0F,1.7F,-1.7F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(6.0,2.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidSphere(1.5F,0.7F,-0.8F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(2.0,2.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidSphere(1.5F,0.7F,0.2F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(-2.0,2.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidSphere(1.5F,0.2F,-0.2F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(-6.0,2.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidSphere(1.0F,1.7F,-1.7F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(6.0,6.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidCylinder(1.5F,1.2F,-1.2F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(2.0,6.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidCylinder(1.5F,0.5F,-0.5F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(-2.0,6.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidCylinder(1.5F,0.5F,-0.0F);
RiIdentity();
RiTranslate(-6.0,6.0,0.0);
RiRotate(-120.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidCylinder(1.0F,0.5F,-0.0F);
}
void main(void) {
RiBegin(RI_NULL);
RiFormat(400,400,1.0F);
RiDisplay("Wedges.tif",
RI_FILE,RI_RGB,
RI_NULL);
RiLightSource("distantlight",RI_NULL);
RiProjection("orthographic",RI_NULL);
RiTranslate(0.0F,0.0F,15.0F);
RiScale(0.12F,0.12F,0.12F);
RiWorldBegin();
RiSurface("matte",RI_NULL);
Go();
RiWorldEnd();
RiEnd();
}
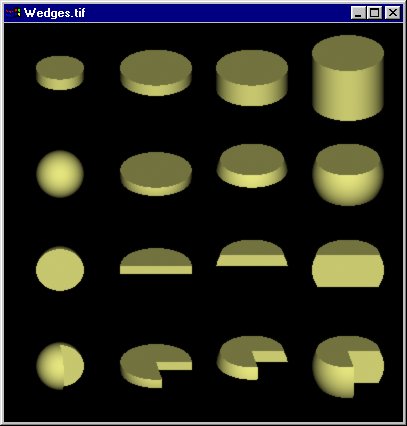
/* Copyrighted Pixar 1989 */
/* From the RenderMan Companion */
#include <ri.h>
#include <math.h>
/* SolidCylinder() makes a solid cylinder
* of the given r,extending
* from zmin to zmax along the z axis. */
void SolidCylinder(float r,
float zmin,
float zmax) {
RiSolidBegin(RI_PRIMITIVE);
RiCylinder(r,zmin,zmax,
360.0,RI_NULL);
RiDisk(zmax,r,360.0,RI_NULL);
RiDisk(zmin,r,360.0,RI_NULL);
RiSolidEnd();
}
/* SolidSphere: create a closed sphere */
void SolidSphere(float r,
float zmin,
float zmax) {
RiSolidBegin(RI_PRIMITIVE);
RiSphere(r,zmin,zmax,360.0,RI_NULL);
if ( fabs(zmax) < r )
RiDisk(zmax,
(float) sqrt(r*r-zmax*zmax),
360.0F,RI_NULL);
if ( fabs(zmin) < r )
RiDisk(zmin,
(float) sqrt(r*r-zmin*zmin),
360.0F,RI_NULL);
RiSolidEnd();
}
/* SolidHemisphere: create a solid
* hemisphere from a sphere
* and a cylinder*/
void SolidHemisphere(float r,
float zmin,
float zmax) {
RiSolidBegin(RI_INTERSECTION);
SolidSphere(r,zmin,zmax);
RiRotate(90.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
SolidCylinder(r,0.0,r);
RiSolidEnd();
}
/* SolidWedge(r,zmin,zmax,thetamax):
* make a solid from a (partial)
* sphere as the intersection or
* union of two hemispheres. */
void SolidWedge(float r,
float zmin,
float zmax,
float thetamax) {
if (thetamax == 180.0) {
SolidHemisphere(r,zmin,zmax); }
else
if (thetamax == 360.0) {
SolidSphere(r,zmin,zmax); }
else
if (thetamax < 180.0) {
RiSolidBegin(RI_INTERSECTION);
SolidHemisphere(r,zmin,zmax);
RiRotate(thetamax-180.0F,
0.0F,0.0F,1.0F);
SolidHemisphere(r,zmin,zmax);
RiSolidEnd(); }
else
if (thetamax < 360.0) {
RiSolidBegin(RI_UNION);
SolidHemisphere(r,zmin,zmax);
RiRotate(thetamax,0.0,0.0,1.0);
SolidHemisphere(r,zmin,zmax);
RiSolidEnd(); }
}
void SolidCone(RtFloat height,RtFloat r) {
RiSolidBegin(RI_PRIMITIVE);
RiCone(height,r,360.0,RI_NULL);
RiDisk(0.0,r,360.0,RI_NULL);
RiSolidEnd();
}
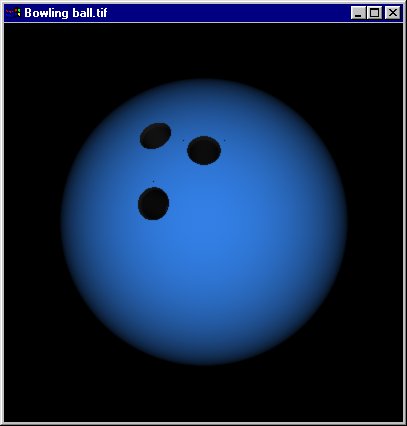
void BowlingBallPlug(void) {
RiSolidBegin(RI_UNION);
SolidCylinder(0.03F,-0.3F,-0.15F);
RiTranslate(0.0,0.0,-0.315F);
SolidCone(0.075F,0.045F);
RiSolidEnd();
}
void BowlingBall(void) {
RtColor ballcolor = { 0.2F,0.5F,0.9F };
RtColor plugcolor = { 0.1F,0.1F,0.1F };
RiSolidBegin(RI_DIFFERENCE);
RiAttributeBegin();
RiSolidBegin(RI_PRIMITIVE);
RiColor(ballcolor);
RiSphere(0.3F,-0.3F,0.3F,360.0F,RI_NULL);
RiSolidEnd();
RiAttributeEnd();
RiSolidBegin(RI_UNION);
RiColor(plugcolor);
RiRotate(170.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
BowlingBallPlug();
RiSolidBegin(RI_UNION);
RiRotate(30.0,-1.0,1.0,0.0);
BowlingBallPlug();
RiRotate(30.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
BowlingBallPlug();
RiSolidEnd();
RiSolidEnd();
RiSolidEnd();
}
void Go(void) {
RiRotate(-135.0F,1.0F,0.0F,0.0F);
RiScale(20.0F,20.0F,20.0F);
BowlingBall();
}
void main(void) {
RiBegin(RI_NULL);
RiFormat(400,400,1.0F);
RiDisplay("Bowling ball.tif",
RI_FILE,RI_RGB,RI_NULL);
RiLightSource("distantlight",RI_NULL);
RiProjection("orthographic",RI_NULL);
RiTranslate(0.0F,0.0F,15.0F);
RiScale(0.12F,0.12F,0.12F);
RiWorldBegin();
RiSurface("matte",RI_NULL);
Go();
RiWorldEnd();
RiEnd();
}
Instanciation d'objets
Renderman permet la création de modèles prédéfinis d'objet ainsi que l'intanciation de ces objets pour leur introduction dans une scène.
RiObjectHandle RiOjectBegin()
-> Début de la définition d'un objet
RtVoid RiOjectEnd()
-> Fin de la définition d'un objet
Tous les objets définis entre ces deux instructions font partie du modèle prédéfini. Celui-ci est référencé par le RtObjectHandle rendu par RiObjectBegin. A ce niveau, l'objet n'existe donc pas encore.
RtVoid RiOjectInstance(RiObjectHandle obj)
-> Instanciation du modèle obj
Un objet de modèle obj est ajouté à la scène.
Exemple 1
/* Copyright Pixar 1989 */
#include <ri.h>
#define L -.5
#define R .5
#define D -.5
#define U .5
#define F .5
#define N -.5
void UnitCube(void) {
static RtPoint Cube[6][4] = {
{ {L,D,F},{L,D,N},{R,D,N},{R,D,F} },
{ {L,D,F},{L,U,F},{L,U,N},{L,D,N} },
{ {R,U,N},{L,U,N},{L,U,F},{R,U,F} },
{ {R,U,N},{R,U,F},{R,D,F},{R,D,N} },
{ {R,D,F},{R,U,F},{L,U,F},{L,D,F} },
{ {L,U,N},{R,U,N},{R,D,N},{L,D,N} } };
for( int i = 0 ; i < 6 ; i++ )
RiPolygon((RtInt) 4,RI_P,
(RtPointer) Cube[i],
RI_NULL);
}
void ColorCube(int n,float s)
{ int x,y,z;
RtColor color;
RtObjectHandle cube;
if ( n <= 0 )
return;
cube = RiObjectBegin();
UnitCube();
RiObjectEnd();
RiAttributeBegin();
RiTranslate(-.5,-.5,-.5);
RiScale(1.0F/n,1.0F/n,1.0F/n);
for( x = 0; x < n ; x++ )
for( y = 0 ; y < n ; y++ )
for( z = 0 ; z < n ; z++ ) {
color[0] = ((float) x+1) / n;
color[1] = ((float) y+1) / n;
color[2] = ((float) z+1) / n;
RiColor(color);
RiTransformBegin();
RiTranslate(x+.5F,y+.5F,z+.5F);
RiScale(s,s,s);
RiObjectInstance(cube);
RiTransformEnd(); }
RiAttributeEnd();
}
void main(void) {
RiBegin(RI_NULL);
RiFormat(256,256,1.0F);
RiDisplay("Instanciation.tif",
RI_FILE,RI_RGB,RI_NULL);
RiLightSource("distantlight",RI_NULL);
RtFloat fov = 45.0F ;
RiProjection("perspective",RI_FOV,
(RtPointer) &fov,RI_NULL);
RiTranslate(0.0F,0.0F,2.2F);
RiRotate(60.0F,-1.0F,1.0F,0.0F);
RiWorldBegin();
RiSurface("matte",RI_NULL);
ColorCube(6,0.9F);
RiWorldEnd();
RiEnd();
}

Exemple 2
/* Copyrighted Pixar 1989 */
/* From the RenderMan Companion */
#include <ri.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
typedef struct { RtFloat x,y;} Point2D;
#define NPOINTS 10
#define NU 13
#define MAXNPTS 100
#define F .5522847F
Point2D points[NPOINTS] = {
{.0000F,1.5000F},
{.0703F,1.5000F},
{.1273F,1.4293F},
{.1273F,1.3727F},
{.1273F,1.2300F},
{.0899F,1.1600F},
{.0899F,1.0000F},
{.0899F,0.7500F},
{.4100F,0.6780F},
{.1250F,0.0000F}};
float cf[NU][2] = {
{ 1.0F,0.0F },{ 1.0F,F },
{ F,1.0F },{ 0,1.0F },
{-F,1.0F },{-1.0F,F },
{-1.0F,0.0F },{-1.0F,-F },
{-F,-1.0F },{ 0,-1.0F },
{ F,-1.0F },{ 1.0F,-F },
{ 1.0F,0} };
RtPoint mesh[MAXNPTS][NU];
RtColor color = {.9F,.9F,.5F};
void SurfOR(Point2D pts[],int npoints) {
for ( int v = 0 ; v < npoints ; v++) {
for ( int u = 0 ; u < NU ; u++ ) {
mesh[v][u][0] = pts[v].x*cf[u][0];
mesh[v][u][1] = pts[v].x*cf[u][1];
mesh[v][u][2] = pts[v].y; } }
RiBasis(RiBezierBasis,
RI_BEZIERSTEP,
RiBezierBasis,
RI_BEZIERSTEP);
RiPatchMesh(RI_BICUBIC,
(RtInt) NU,
RI_NONPERIODIC,
(RtInt) npoints,
RI_NONPERIODIC,
RI_P,(RtPointer) mesh,
RI_NULL);
}
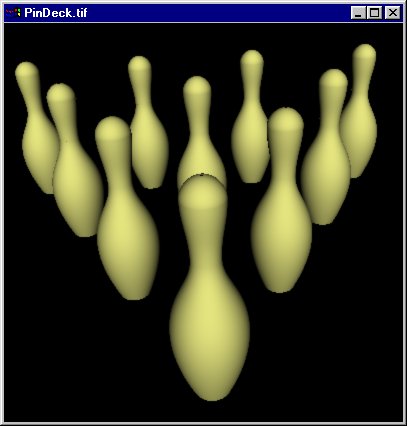
void BowlingPin(void) {
SurfOR(points,NPOINTS);
}
void PlacePins(RtFloat xseparation,
RtFloat yseparation) {
int row,pin;
RtObjectHandle phandle;
phandle = RiObjectBegin();
if (!phandle)
return;
BowlingPin();
RiObjectEnd();
RiColor(color);
for (row = 0; row < 4; row++) {
RiTransformBegin();
RiTranslate(row*xseparation,
row*yseparation/2,
0.0);
for ( pin = 0 ; pin <= row ; pin++ ) {
RiTransformBegin();
RiTranslate(0.0,
-pin * yseparation,
0.0);
RiObjectInstance(phandle);
RiTransformEnd(); }
RiTransformEnd(); }
}
void Go(void) {
RiRotate(3.0F,0.0F,0.0F,1.0F);
RiRotate(-120.0F,1.0F,0.0F,0.0F);
RiRotate(-90.0F,0.0F,0.0F,1.0F);
RiTranslate(-3.0F,0.0F,0.5F);
PlacePins((float) (1.2*
sin(60.0*3.14159/180.0)),
1.2F);
}
void main(void) {
RiBegin(RI_NULL);
RiFormat(400,400,1.0F);
RiDisplay("PinDeck.tif",
RI_FILE,RI_RGB,RI_NULL);
RiLightSource("distantlight",RI_NULL);
RtFloat fov = 45.0F ;
RiProjection("perspective",
RI_FOV,(RtPointer) &fov,
RI_NULL);
RiTranslate(0.0F,0.0F,6.0F);
RiWorldBegin();
RiSurface("matte",RI_NULL);
Go();
RiWorldEnd();
RiEnd();
}
La caméra digitale
Introduction
/* Copyrighted Pixar 1989 */
#include <ri.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void main(void) {
RiBegin(RI_NULL);
RiLightSource("distantlight",RI_NULL);
RiDisplay("ri.tiff",RI_FILE,
RI_RGBA,RI_NULL);
RiFormat((RtInt) 400,(RtInt) 300,-1.0);
RiCropWindow(0.0,1.0,0.0,1.0);
RiScreenWindow(-1.3333F,1.33333F,
-1.0F,1.0F);
RtFloat fov = 25;
RiProjection("perspective",
RI_FOV,(RtPointer) &fov,
RI_NULL);
RiWorldBegin();
RiTranslate(0.0,0.0,5.0);
RiRotate(10.0,0.0,0.0,1.0);
RiRotate(-30.0,0.0,1.0,0.0);
RiRotate(40.0,1.0,0.0,0.0);
RiTorus(0.75F,0.4F,0.0F,
360.0F,360.0F,RI_NULL);
RiWorldEnd();
RiEnd();
}
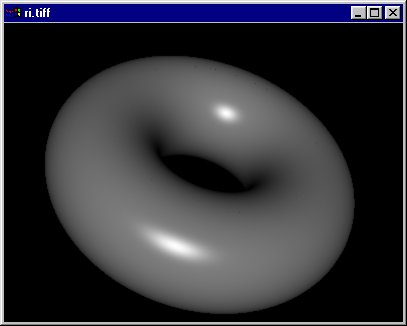
Ce programme définit une caméra digitale qui est ensuite appliquée à une scène simple pour générer une image.
Caractéristiques de l'image
RiDisplay(char *name,RtToken type,RtToken mode,param);
Définition du nom et du type du périphérique d'affichage (un fichier TIFF 24 bits)
RiFormat(RtInt xres,RtInt yres,RtFloat pixelaspectratio);
Définition de la résolution de l'image générée
RiCropRegion(RtFloat xg,RtFloat yt,RtFloat xd,RtFloat yb);
Définition de la portion d'image affichée
Caractéristiques de la caméra
Définition de taille et de la position de la fenêtre écran
Projection
Utilisation d'une projection en perspective avec un angle d'ouverture de fo degrés
Placement de la caméra
Par rotation et translation, la caméra digitale est placée en position et en orientation.
Les valeurs par défaut sont (0,0,0) pour la position et (0,0,1) pour la direction.
Exemple
/* Copyrighted Pixar 1989 */
#include <math.h>
#include <ri.h>
#define PI 3.14159265359
void PlaceCamera(RtPoint pos,
RtPoint dir,
float roll) {
RiIdentity();
RiRotate(-roll,0.0,0.0,1.0);
AimZ(dir);
RiTranslate(-pos[0],-pos[1],-pos[2]);
}
void AimZ(RtPoint dir) {
double xzlen, yzlen, yrot, xrot;
if ( ( direction[0] == 0 )
&& ( direction[1] == 0 )
&& ( direction[2] == 0 ) )
return;
xzlen = sqrt(dir[0]*dir[0]+dir[2]*dir[2]);
if (xzlen == 0)
yrot = ( dir[1] < 0 ) ? 180 : 0;
else
yrot = 180*acos(dir[2]/xzlen)/PI;
yzlen = sqrt(dir[1]*dir[1]+xzlen*xzlen);
xrot = 180*acos(xzlen/yzlen)/PI;
if ( dir[1] > 0 )
RiRotate(xrot,1.0,0.0,0.0);
else
RiRotate(-xrot,1.0,0.0,0.0);
if ( dir[0] > 0 )
RiRotate(-yrot,0.0,1.0,0.0);
else
RiRotate(yrot,0.0,1.0,0.0);
}
Caractéristiques de la caméra
Un certain nombre de fonctions contrôlent les caractéristiques de la caméra digitale de Renderman.
Plans de clipping
Choix du mode de projection
Définition de la fenêtre écran
L'affichage
Illumination et ombrage
Manipulation de l'apparence des objets:
placement de lumières,
colorisation avec autre chose que des couleurs unies.
Quand un point doit être affiché, évaluation de trois paramètres:
l'illumination: intensité et couleur de la lumière qui le touche,
les réflexion et transmission: calcul de l'intensité et de la couleur de la lumière réfléchie vers l'observateur,
les effets atmosphériques: modification de la couleur de la lumière quand elle transite d'un objet vers l'observateur.